Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a cannabinoid substance discovered in cannabis and hemp plants. It's chemically comparable to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) but with some crucial differences. Here's whatever you need to learn about THCV including the threats, advantages, distinctions, and similarities with other forms of THC and more. What Is THCV? THCV is a less common cannabinoid discovered in some pressures of marijuana, particularly African sativa.
 What is THCv? THCv Effects Verilife
What is THCv? THCv Effects Verilife
 What is THCV and what are the benefits of this cannabinoid? Leafly
What is THCV and what are the benefits of this cannabinoid? Leafly
 What Is THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)? - CNBS
What Is THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)? - CNBS
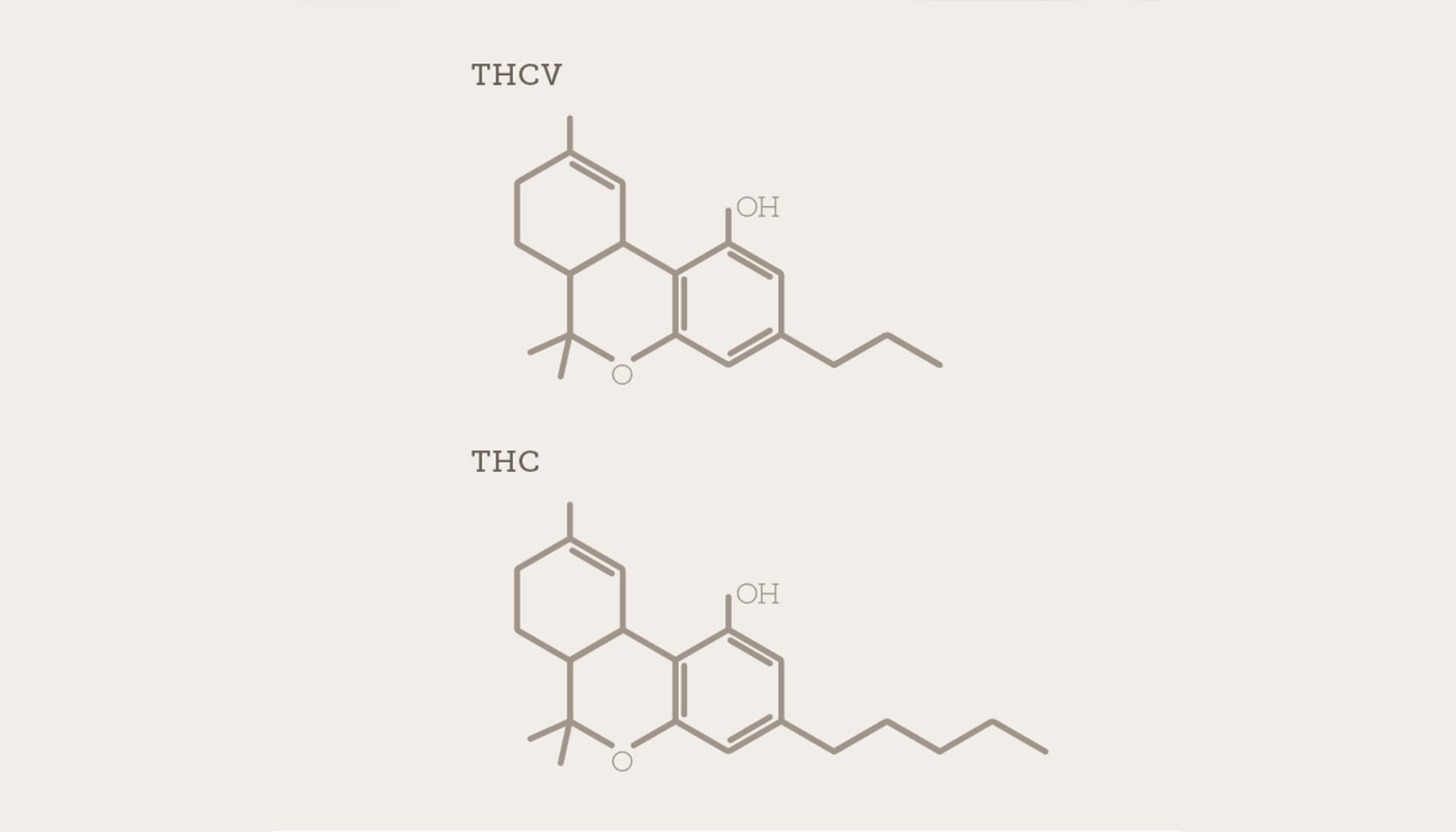
THCV has a 3-carbon side chain instead of THC's 5-carbon side chain. This distinction is subtle, but it has an obvious impact on the effect profile. THCV is somewhat psychedelic but only about and about. What Does THCV Feel Like? THCV has a strong energy-boosting element to it, that makes it specifically popular amongst students and athletes.
In the United States, THCV regulation is nuanced. THCV is not a Schedule I Drug, but marijuana extracts are making it somewhat unclear what the federal position is on THCV. The 2018 Farm Costs specifies that hemp plants and all derivatives of the plants are legal on a federal level, numerous business abide by this law and still supply THCV to consumers by only extracting the substance from hemp plants.
If THCV is considered a THC analog, it might be controlled in the future by the same guidelines as THC under the Federal Analog Act. This act specifies that any substance that shares a comparable molecular profile as a recognized prohibited compound it's included in the very same drug Arrange classification.
What Are the Results of THCV? Advocates of THCV report that it produces an intense burst of energy and makes them feel blissful without the mental cloudiness triggered by THC. The impacts are extremely moderate compared to THC. The impacts are practically solely cognitive yet somehow have extremely little influence on headspace.
2. THCV & Appetite Some THCV users claim that it curbs their hunger. This is a typical result of other focus-enhancing substances also. It's as though THCV eliminates the distraction of other bodily procedures (like hunger) in order to preserve resources and attention to cognitive tasks instead. How Does THCV Work? Cannabinoids produce biological results in the body by interacting with endocannabinoid receptors.
CB1 receptors lie in the nervous system and communicate with neurotransmitters in the brain to produce mind-altering effects. Interaction with CB1 sites is what offers some cannabinoids like THC their psychoactivity. THCV is a bit challenging to understand since it's mainly a CB1 villain, indicating it has the opposite result as THC.
While scientists are still seeking to understand this procedure, it appears THCV is able to block the results of CB1 in low doses and promote them in high dosages. CB2 receptors are discovered mostly in the immune system. THCV is a partial agonist of CB2, but the effects of this partial activity aren't well-known, and it relatively has no discernible impact on THCV users' experience.
As mentioned in the previous area, THCV is a CB1 antagonist in low doses which is the exact opposite effect of delta 8 and delta 9 THC. This could mean that THCV neutralizes some of the psychedelic impacts of THC. This result could explain why individuals who utilize THCV feel so clear-headed specifically compared to the well-known "fogginess" induced by delta 9 THC.